Privacy-Enhancing Computation: Data Protection Technology
It’s no gainsaying that everything about life; business, academics, politics and governance, health, finance, and the economy, the entirety of life are decibels of data strung together to make for a whole. Now, the compromise of any part of data is a major threat to the whole. This is the reason data protection ought to be taken more seriously and given the utmost priority than it’s ever been received. The vulnerability of data predisposes it to malicious attacks often leading to data theft, and privacy breach despite legislations such as the EU’s GDPR and other national data protection laws.
The integration of technology into data collection, use, and governance, while a blessing in itself, has further made data more prone to attackers, introduced new threats, and increased the risk of privacy harm. Consumers are becoming skeptical about sharing their data because of the uncertainty of who uses them, how, and for what purpose their data are used. These concerns have further necessitated the need for a more urgent and proactive data security measures such as the privacy-enhancing computation (PEC) and technologies (PET) which allows for the secured, structured, and controlled management and usage of data.
Privacy Enhancing Technologies Explained
While there is no definite definition for PETs, the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) describes privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) as “software and hardware solutions, i.e., systems encompassing technical processes, methods, or knowledge to achieve specific privacy or data protection functionality or to protect against risks to the privacy of an individual or a group of natural persons” (European Union Agency for Network and Information Security, 2015). So, you want to think of PETs as a wide variety of technologies and techniques that protect individuals’ privacy at the highest level possible by minimizing or eliminating the collection and processing of personally identifiable information (PII) and empowers people in the long run. According to the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO), “PETs are particularly suitable in contexts that involve large-scale collection and analysis of personal data, such as artificial intelligence applications, Internet of Things, and cloud computing services” (ICO, 2022).
Examples of PETs include encryption, anonymous communication tools, digital signatures, and privacy-focused search engines (Duality, 2023)
PETs are also referred to as partnership enhancing technologies and trust technologies because not only do they enhance personal privacy in data utilization process, they also promote collaboration by reducing the risk associated with data sharing among organizations.
Privacy enhancing technologies (PETs) have become widely acclaimed and accessible given recent technological advances such as the proliferation of artificial intelligence (AI) machine learning (Ml) systems, the rise of the data economy, support from policymakers, and increased privacy awareness among consumers (ISACA, 2024). PETs enable the responsible use of data in tandem with data protection regulations. They also help people retain control over their personal data while protecting them against privacy violations such as, unauthorized access or usage, loss, and identify theft.
Simultaneously, privacy-enhancing computation (PEC) leverages technologies that enforce data privacy and security. It enables data sharing while maintaining the security and privacy of both the data and the process involved. PEC takes three forms comprising corresponding technologies that enable data processing and application without compromising the security of data and the privacy of data contributors.
- The first includes technologies that provide a trusted environment where data can be processed securely.
- The second form includes technologies such as federated machine learning and privacy-aware machine learning that support processing and analytics.
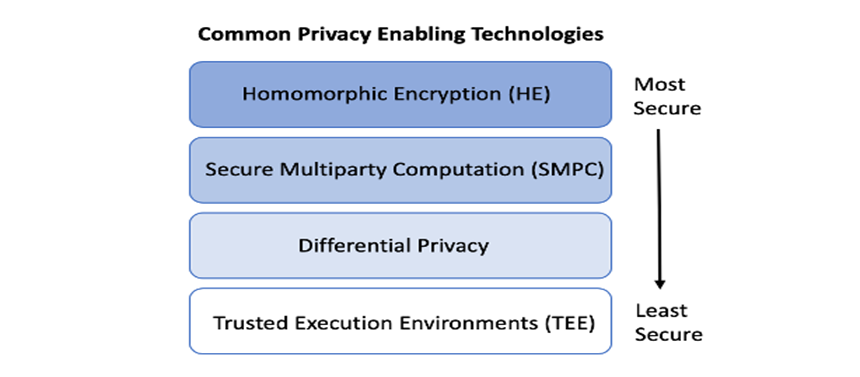
- The third form entails technology enabling data and algorithms transformation including homomorphic encryption which keeps data confidential, multiparty computation, differential privacy, and private set intersection.
The Benefits of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
The lifeline of any organization is its data; its operations and growth largely depend on it. Even more the relevance of any business depends on how it is able to manage data and assure of its security and privacy because failure to do so can expose organizations to cyber threats, litigations, reputational damage, and potential harm to even the data contributors themselves. Hence, we present reasons why every organization should take investing in privacy-enhancing technologies seriously.
Personal Information Protection: PETS reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access by ensuring that the data collected and processed are well secured. This also protects the privacy of data contributors and helps companies avoid litigations and reputational damage. Privacy-enhancing technologies such as anonymization techniques protect personal information by removing personally identifiable information (PII) such as names, addresses, and phone numbers from user data. Also, differential privacy works by adding background noise to data to make it difficult to identify individual users. Personal information can also be secured through homomorphic encryption for data encryption (Figas, 2024).
Data Accuracy and Validation: Businesses can validate their data collection and processing practices and improve their data accuracy through PETs for effective applications.
Secure Data Sharing: PETs can be used to enable secure data sharing and collaboration between different organizations without the depletion of data value or the compromise of user privacy. This can be carried out through techniques, such as secure multi-party computation (MPC) or homomorphic encryption, which allow multiple parties to perform computations on encrypted data without revealing the underlying data (Figas, 2024).
Regulatory Compliance: PETs enable organizations to adopt privacy-preserving practices that safeguard sensitive data, while allowing them to comply with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) which require companies to implement specific privacy protections and disclose how data is collected and used thereby preventing lawsuits and fines while securing user privacy.
Customer Trust Retention: Customers and other data contributors repose confidence in organizations that demonstrate transparency in how they collect and use their data. When businesses deploy privacy-enhancing technologies, they prove their commitment to user privacy and data protection. For instance, companies can enact privacy policies that state their data collection and management practices, and also give contributors control over their data. Organizations can also obtain user consent through opt-in or opt-out mechanisms, depending on the type of data being collected.
Cost Reduction: Businesses can leverage PETs to reduce the costs of maintaining large and complex tech infrastructure required for data storage and processing. The financial implications of data breaches can also be reduced with privacy-enhancing technologies.
Although privacy-enhancing technologies have been in existence before now, they have only recently been deployed to real-life applications. They have emerged from advanced research and are gaining industry adoption via commercial offerings and open-source solutions, lowering the cost barrier for implementation. PETs are used during data collection and usage, online transactions, and other communication processes to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and data authenticity (Duality, 2023).
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the potentials that privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) offer, there are also several challenges that must be addressed for their effective implementation. These challenges can range from technical and financial to legal.
Lack of Standard: The lack of universal standards for PETs can hinder their adoption and interoperability. The standardization of PETs will ensure that they are effective and consistent across specific sectors.
Complexity: Understanding and applying privacy-enhancing technologies can be complicated as specialized knowledge and skills may be required to run them.
Trade-Offs and Balance: Deploying PETs can require trade-offs between privacy and other concerns, such as the accuracy of data. Thus, businesses may need to balance the benefits of PETs with other priorities, such as other legitimate business goals.
Cost: The adoption and maintenance of PETs can be costly. The cost of implementing PETs can include the purchase of hardware and software, integrations with workflows, employee training, as well as, regular maintenance and updates.
Conclusion
The realities that advanced technology and AI-driven innovations present have had organizations investing in technologies that can enable them to enforce data privacy, security, reduce risks, and retain customers’ trust. At Telliswall, we understand the importance of data protection and privacy to your organizational operations and success, so, you can rely on us to deliver on custom end-to-end solutions that meet your specific business needs. We bring the expertise and experience that support your collection, processing, analysis, and utilization of data while safeguarding the confidentiality and privacy of your clients.
References
Duality (2023). Privacy Enhancing Technologies https://dualitytech.com/glossary/privacy-enhancing-technologies/
E-Spin (2023). Emergence of Privacy-Enhancing Computation: Enhancing Data Privacy and Security https://www.e-spincorp.com/emergence-of-privacy-enhancing-computation-enhancing-data-privacy-and-security/
European Union Agency for Network and Information Security (2015). Readiness Analysis for the Adoption and Evolution of Privacy Enhancing Technologies: Methodology, Pilot Assessment and Continuity Plan https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/pets/view/++widget++form.widgets.fullReport/@@download/Readiness+Analysis+for+the+Adoption+and+Evolution+of+Privacy+Enhancing+Technologies.pdf
Figas, N. (2024). The Benefits of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) in AdTech https://clearcode.cc/blog/benefits-privacy-enhancing-technologies-adtech/
Information Commissioner’s Office (2022). ICO Publishes Guidance on Privacy Enhancing Technologies https://ico.org.uk/about-the-ico/media-centre/news-and-blogs/2022/09/ico-publishes-guidance-on-privacy-enhancing-technologies/
ISACA (2024).Exploring Practical Considerations and Applications for Privacy Enhancing Technologies https://www.isaca.org/resources/white-papers/2024/exploring-practical-considerations-and-applications-for-privacy-enhancing-technologies
Lundy-Bryan, L. (2021). “Privacy Enhancing Technologies: Part 2—The Coming Age of Collaborative Computing,” Lunar Ventures: Insight Series https://www.kisacoresearch.com/sites/default/files/documents/pet_white_paper_part_2_-_the_coming_age_of_collaborative_computing10992.pdf
Tsaaro Consulting (2024). The Rise of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) in a Data-Driven World https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/rise-privacy-enhancing-technologies-pets-data-driven-world-tsaaro-9cmqf